The Rise of Cloud-Based Operating Systems: Are They the Future?
The Rise of cloud-based operating systems is rapidly transforming how we interact with technology. This blog post delves into the core of cloud OS, exploring its benefits such as enhanced accessibility, scalability, and simplified management. A detailed analysis examines the factors driving its increasing popularity, highlighting practical applications and real-world examples across various industries. We’ll also look at future trends shaping the evolution of cloud OS and provide actionable steps for businesses and individuals looking to embrace this innovative technology. Understanding the transformative potential of cloud OS is crucial for staying ahead in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Understanding Cloud-Based OS: Benefits And Key Features
Cloud-based operating systems represent a significant shift in how we interact with technology. Unlike traditional operating systems installed directly on a device, cloud-based OS resides on remote servers and are accessed via the internet. This fundamental difference unlocks a range of benefits, but also introduces unique considerations. The rise of these systems is closely tied to advancements in cloud computing and network infrastructure, making them a viable alternative for many users and organizations.
| Feature | Traditional OS | Cloud-Based OS |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Locally installed on hardware | Accessed remotely via internet |
| Storage | Local storage on device | Cloud storage |
| Updates | Manual or scheduled updates | Automatic updates on server-side |
| Accessibility | Limited to the device | Accessible from any device with internet |
One of the primary advantages of a cloud-based OS is its accessibility. Users can access their desktop environment and applications from virtually any device with an internet connection. This is particularly useful for individuals who work across multiple devices or need to access their work from different locations. Furthermore, data stored in the cloud is typically more secure than data stored locally, as cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and data redundancy.
- Key Benefits of Cloud-Based OS
- Accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Automatic updates and maintenance managed by the provider.
- Enhanced security measures for data protection.
- Scalability to adjust resources based on needs.
- Cost-effective solution compared to traditional OS licensing.
However, it’s important to acknowledge the dependencies of cloud-based OS. A stable and reliable internet connection is crucial for seamless operation. Downtime or connectivity issues can disrupt workflow and limit access to applications and data. Organizations considering adopting a cloud-based OS should carefully evaluate their network infrastructure and plan for potential disruptions.
Beyond accessibility, cloud-based operating systems offer several key features that enhance user experience and streamline IT management. Automatic updates ensure that users always have the latest software versions without manual intervention. Centralized management simplifies tasks such as software deployment, user provisioning, and security patching. These features collectively reduce IT overhead and improve overall efficiency.
Exploring The Rise Of Cloud OS: A Detailed Analysis
The adoption of cloud-based operating systems is rapidly transforming the IT landscape, driven by the increasing demand for scalable, accessible, and cost-effective computing solutions. Unlike traditional operating systems that are installed locally on physical hardware, cloud OS resides on remote servers, allowing users to access their applications and data from any device with an internet connection. This shift represents a fundamental change in how businesses and individuals manage their digital resources, offering unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. Cloud OS solutions are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with enhanced features for security, collaboration, and resource management.
| Feature | Traditional OS | Cloud OS |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Limited to local device | Accessible from any device with internet |
| Scalability | Hardware-dependent, difficult to scale | Highly scalable, on-demand resources |
| Maintenance | Manual updates and maintenance | Automated updates and maintenance |
| Cost | High upfront costs, ongoing maintenance | Lower upfront costs, pay-as-you-go model |
One of the key factors fueling the rise of cloud OS is the ability to streamline IT operations. With a cloud OS, organizations can centralize their computing infrastructure, reducing the burden on local hardware and IT staff. This centralization facilitates easier management of software updates, security patches, and data backups, minimizing the risk of downtime and data loss. Furthermore, cloud OS environments often come with built-in monitoring and analytics tools, providing valuable insights into system performance and resource utilization. This allows businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure and make data-driven decisions.
However, the transition to a cloud OS is not without its challenges. Organizations must carefully consider various factors, including network connectivity, data security, and regulatory compliance. A reliable and high-speed internet connection is essential for ensuring a seamless user experience, while robust security measures are needed to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Additionally, businesses operating in regulated industries may need to implement specific controls to comply with data privacy and security requirements. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of cloud OS, such as increased agility, reduced costs, and improved collaboration, make it an attractive option for many organizations.
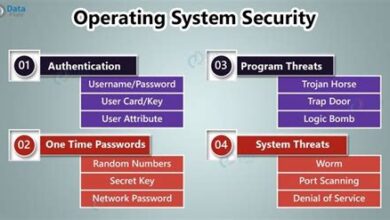
Security Considerations
Security remains a paramount concern when adopting a cloud OS. Organizations must ensure that their data is protected from unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, and access controls are essential steps in securing a cloud OS environment. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments can also help identify and address potential weaknesses.
- Steps to Migrate to a Cloud OS
- Assess your current IT infrastructure and identify the applications and data that can be migrated to the cloud.
- Choose a reputable cloud OS provider that meets your security, compliance, and performance requirements.
- Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources needed for the transition.
- Implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems.
- Conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure that the migrated applications and data function correctly in the cloud environment.
- Train your IT staff and end-users on how to use the cloud OS and its features.
- Continuously monitor and optimize the cloud OS environment to ensure optimal performance and security.
Performance Benchmarks
Evaluating the performance of a cloud OS is critical for ensuring that it meets the needs of the organization. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as response time, throughput, and resource utilization should be monitored and analyzed. Conducting performance benchmarks can help identify bottlenecks and optimize the cloud OS environment for maximum efficiency. Performance benchmarks also help in understanding how well the cloud OS scales under increasing workloads.
Cost Analysis
A thorough cost analysis is essential for determining the financial viability of adopting a cloud OS. While cloud OS solutions often offer lower upfront costs compared to traditional operating systems, organizations must also consider ongoing costs such as subscription fees, data storage charges, and network bandwidth usage. A detailed cost-benefit analysis can help organizations make informed decisions about whether to migrate to a cloud OS. A cost analysis should also factor in potential savings from reduced IT infrastructure and maintenance.
The shift to cloud-based operating systems is not just a technological evolution; it’s a strategic imperative for businesses looking to thrive in the digital age. The ability to scale resources on demand, reduce IT overhead, and enhance collaboration makes cloud OS an indispensable tool for modern organizations. – Tech Industry Analyst
Okay, I will create a content section for your article The Rise of Cloud-Based Operating Systems: Are They the Future? focusing on The Rise, with the title Cloud Operating Systems: Practical Applications And Examples. html
Cloud Operating Systems: Practical Applications And Examples
Cloud operating systems are rapidly transforming how businesses and individuals interact with technology. Unlike traditional operating systems that reside on local hardware, cloud OS platforms operate remotely, delivering computing resources and services over the internet. The rise of these systems is fueled by their ability to offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s explore some practical applications and examples of cloud operating systems to understand their real-world impact.
One significant area where cloud operating systems shine is in virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI). VDI allows organizations to host desktop environments on centralized servers, which users can then access from any device with an internet connection. This is particularly beneficial for companies with remote workers or those that need to ensure data security. By centralizing the OS and applications, IT departments can easily manage updates, security patches, and software deployments, reducing the burden on individual users and enhancing overall system security. Below is a table to show key vendors in the market.
| Vendor | Cloud OS Offering | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| VMware | VMware Horizon | Centralized management, instant clones, application delivery |
| Citrix | Citrix Virtual Apps and Desktops | HDX technology, application virtualization, secure access |
| Microsoft | Windows 365 | Cloud PC, simplified management, integration with Microsoft 365 |
| Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Amazon WorkSpaces | Pay-as-you-go pricing, persistent desktops, broad device support |
Cloud operating systems are also widely used in development and testing environments. Developers can quickly provision virtual machines (VMs) with pre-configured operating systems and development tools, allowing them to start coding and testing applications without the overhead of setting up local environments. This accelerates the development lifecycle and enables teams to collaborate more effectively. Consider the many benefits of adopting a cloud OS:
- Rapid Provisioning: Quickly deploy and scale resources as needed.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the resources you consume.
- Collaboration: Enable seamless teamwork across distributed teams.
- Version Control: Maintain consistent environments across all stages of development.
- Disaster Recovery: Ensure business continuity with built-in backup and recovery mechanisms.
Furthermore, cloud operating systems facilitate the delivery of Software as a Service (SaaS) applications. SaaS providers rely on cloud infrastructure to host their applications and deliver them to users over the internet. This model allows users to access software from anywhere without the need for local installation or maintenance. The rise of SaaS has revolutionized industries such as CRM, HRM, and project management, making sophisticated tools accessible to businesses of all sizes. As cloud technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications of cloud operating systems to emerge, driving efficiency, flexibility, and growth across various sectors.
Future Trends And Actionable Steps For Cloud OS Adoption
As we look ahead, the rise of cloud-based operating systems is poised to reshape how we interact with technology. Several key trends are emerging that will drive further adoption and innovation in this space. We can anticipate enhanced integration with AI and machine learning, allowing for more personalized and predictive user experiences. Additionally, the focus will likely shift towards more robust security features to address the unique challenges of cloud environments, such as data breaches and unauthorized access. Finally, expect to see greater emphasis on cross-platform compatibility and seamless integration with various devices, enabling users to access their applications and data from anywhere, at any time.
| Feature | Traditional OS | Cloud OS |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Local Hard Drive | Cloud Storage |
| Processing | Local CPU/GPU | Remote Servers |
| Accessibility | Device-Specific | Device-Independent |
| Security | User-Managed | Provider-Managed |
To successfully navigate this transition and leverage the benefits of cloud OS, organizations and individuals need to take proactive steps. This involves assessing current infrastructure, identifying suitable cloud OS solutions, and developing a comprehensive migration strategy. Furthermore, it’s crucial to invest in training and development to equip teams with the skills needed to manage and maintain cloud-based environments effectively. By planning and executing these steps, users can minimize disruption and maximize the value of cloud OS.
Here are some actionable steps that you can take:
- Actionable Steps for Cloud OS Adoption
- Assess your current IT infrastructure and identify areas suitable for cloud migration.
- Research and compare different Cloud OS providers to find the best fit for your needs.
- Develop a detailed migration plan, including data backup and recovery strategies.
- Implement robust security measures, such as multi-factor authentication and encryption.
- Provide comprehensive training for your IT staff on managing and maintaining a Cloud OS environment.
- Monitor performance and optimize resource allocation to ensure efficient operation.
- Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving cloud technologies.
In conclusion, the future of operating systems is undeniably heading towards the cloud. Embracing this shift requires a strategic approach, combining technological innovation with a focus on security, user experience, and cross-platform compatibility. By taking the necessary steps, individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of cloud OS and stay ahead in an increasingly digital world. The key is to stay informed, adapt to new developments, and proactively address the challenges and opportunities that come with this transformative technology. Ultimately, the shift to cloud OS promises a more flexible, scalable, and efficient computing experience for all.