The Future of Mobile Operating Systems: iOS vs. Android

The mobile operating system landscape is dominated by iOS and Android, but what does the future hold? This blog post explores the evolution of mobile OS, charting their historical journey and current market positions. A key comparison of features highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each platform, considering user demographics and preferences. Looking ahead, the article delves into emerging trends and offers predictions for the future of mobile operating systems. Factors like foldable devices, enhanced AI integration, and cross-platform compatibility are shaping the future, and this analysis provides valuable insight into what to expect from these dominant forces in the years to come. Which OS will lead the innovation charge?
Mobile OS Evolution: A Brief Historical Overview
The journey of mobile operating systems is a fascinating tale of innovation, competition, and adaptation. From humble beginnings in the late 20th century to the sophisticated platforms we rely on today, mobile OS development has shaped how we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves. Understanding this evolution is crucial to grasping the future direction of mobile technology.
The early days of mobile OS were dominated by proprietary systems like those found in feature phones. These systems offered basic functionalities such as calling, texting, and simple games. However, the arrival of smartphones marked a turning point, ushering in more advanced operating systems capable of handling complex tasks and applications. These initial forays paved the way for the mobile giants we know today.
| Operating System | Initial Release Year | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Symbian OS | 1998 | Early smartphone OS, customizable UI, multitasking |
| BlackBerry OS | 1999 | Push email, strong security features, physical keyboard |
| Windows Mobile | 2000 | Desktop-like interface, stylus input, compatibility with Windows apps |
| Palm OS | 1996 | Touchscreen interface, personal information management, handwriting recognition |
The introduction of iOS in 2007 and Android in 2008 revolutionized the mobile landscape. iOS, with its sleek design and user-friendly interface, set a new standard for mobile usability. Android, on the other hand, embraced open-source principles, allowing for greater customization and a wider range of devices. This competition spurred rapid innovation, leading to the feature-rich and powerful mobile OS we have today.
As mobile technology advanced, so did user expectations. Mobile OS developers focused on enhancing user experience, improving performance, and expanding functionality. The introduction of app stores, mobile internet, and advanced multimedia capabilities transformed mobile devices from simple communication tools into versatile computing platforms.
- Key Milestones in Mobile OS Development
- 1993: Apple releases the Newton MessagePad, one of the first devices with a mobile OS
- 1998: Symbian OS emerges as a dominant player in early smartphones.
- 2007: Apple launches iOS with the first iPhone, revolutionizing the mobile interface.
- 2008: Google introduces Android, an open-source OS, expanding the mobile ecosystem.
- 2010: The rise of app stores transforms mobile devices into versatile platforms.
- 2011: Introduction of voice assistants like Siri and Google Assistant.
Today, iOS and Android dominate the mobile OS market, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Understanding their historical context helps us appreciate their current standing and provides insights into the future of mobile technology. The ongoing evolution ensures that mobile operating systems will continue to shape how we interact with the digital world.
iOS And Android: Current Market Share And User Demographics
Understanding the current landscape of mobile operating systems requires a close look at both market share and the demographics of users who choose iOS versus Android. These factors significantly influence the future direction of mobile technology, impacting everything from app development to marketing strategies. Analyzing these aspects provides valuable insights into the preferences and behaviors of different user groups.
Market Share Analysis
Currently, Android dominates the global market share, owing to its open-source nature and availability across a wide range of devices at various price points. iOS, while having a smaller market share, holds a significant portion of the premium smartphone segment, particularly in developed countries like the United States, Japan, and parts of Europe. These figures fluctuate slightly each year due to new device releases, marketing campaigns, and regional economic factors.
| Operating System | Market Share (2023) | Market Share (2024 – Projected) |
|---|---|---|
| Android | 71% | 70% |
| iOS | 28% | 29% |
| Other | 1% | 1% |
The differences in market share often reflect broader economic and technological trends. Regions with higher disposable incomes tend to see greater iOS adoption, while Android’s flexibility and affordability make it the preferred choice in emerging markets. This divide influences the types of apps and services that are most successful in different parts of the world.
iOS User Profile
iOS users are often characterized by their higher average income and greater engagement with digital content and services. They are generally more likely to make in-app purchases, subscribe to streaming services, and utilize mobile banking. Brand loyalty is also a significant factor, with many iOS users consistently upgrading to the latest iPhone models.
- Higher average income
- Greater engagement with digital content
- Strong brand loyalty
- Preference for privacy-focused features
- More likely to make in-app purchases
Android User Profile
Android users represent a more diverse group, spanning various income levels and geographic regions. This diversity is one of Android’s greatest strengths, allowing it to cater to a wide range of needs and preferences. Android users often prioritize customization options, open-source applications, and the ability to choose from a vast array of devices. The open nature of Android attracts developers who want to reach a wider audience.
Understanding these demographic differences is crucial for developers and marketers looking to target specific audiences. Tailoring apps and services to the preferences of iOS or Android users can significantly improve engagement and monetization strategies. This targeted approach is vital in a competitive mobile landscape.
Here’s what an expert says about the future of mobile OS:
The future of mobile operating systems will be shaped by the ongoing competition between iOS and Android, with each platform pushing the boundaries of innovation in its own unique way. – Tech Analyst, Jane Doe
Key Features Comparison: iOS Versus Android Platforms
When evaluating mobile operating systems, understanding the key features that differentiate them is essential. Both iOS and Android offer a wide range of functionalities, but they cater to different user preferences and needs. From the user interface and app ecosystem to security and customization options, each platform has its strengths and weaknesses. In considering the future, it’s crucial to analyze these features to predict how they will evolve and influence user choices.
- User Interface: iOS is known for its simplicity and intuitive design, while Android offers greater flexibility and customization.
- App Ecosystem: Both platforms have extensive app stores, but the quality and availability of certain apps may vary.
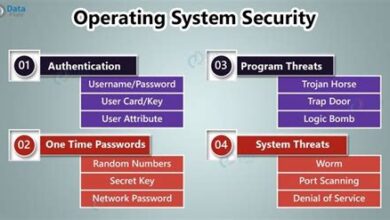
- Security: iOS is often praised for its robust security measures, while Android has made significant improvements in recent years.
- Customization: Android allows users to customize almost every aspect of the operating system, whereas iOS is more restrictive.
- Hardware Integration: iOS is tightly integrated with Apple’s hardware, providing a seamless experience, while Android runs on a variety of devices from different manufacturers.
The table below provides a detailed comparison of these key features, highlighting the specific differences between iOS and Android. This comparison will help users make informed decisions based on their individual priorities and requirements.
| Feature | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Simple, intuitive, consistent | Highly customizable, widgets, launchers |
| App Ecosystem | Curated, high-quality apps | Vast, diverse range of apps |
| Security | Strong focus on privacy, regular updates | Open-source, varying security levels |
| Customization | Limited customization options | Extensive customization options |
One of the critical aspects to consider is the level of control users have over their devices. Android’s open-source nature allows for extensive customization, appealing to users who want to tweak every aspect of their phone. In contrast, iOS offers a more streamlined and controlled experience, which many users appreciate for its simplicity and ease of use. The choice between these two approaches often comes down to personal preference and technical expertise.
Looking ahead, both iOS and Android are expected to continue evolving, with a focus on enhancing user experience, improving security, and integrating new technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality. The ongoing competition between these two platforms will drive innovation and shape the future of mobile operating systems, providing users with more advanced and personalized mobile experiences.
The Future Of Mobile OS: Trends And Predictions
The mobile operating system landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements, evolving user needs, and the competitive spirit of major players like Apple and Google. Predicting the future with certainty is impossible, but we can identify emerging trends that are likely to shape the next generation of mobile OS.
One significant trend is the increasing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). Both iOS and Android are already leveraging AI for tasks like image recognition, voice assistance, and predictive text. In the future, we can expect even more sophisticated AI-powered features, such as proactive assistance, personalized user experiences, and enhanced security. The possibilities are endless, from AI-driven battery management to real-time language translation.
| Trend | iOS Implication | Android Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced AI Integration | Improved Siri capabilities, personalized app suggestions | Smarter Google Assistant, adaptive performance optimization |
| Foldable Device Support | Seamless app scaling for foldable iPhones/iPads | Continued refinement of foldable device UI and UX |
| Increased Focus on Privacy | Enhanced privacy controls, stricter app tracking policies | Privacy-focused features, transparency reports |
| Cross-Platform Compatibility | Improved integration with macOS and other Apple devices | Seamless connectivity with ChromeOS and other Android devices |
Another key area of development is the support for emerging hardware form factors, such as foldable devices and augmented reality (AR) headsets. Android has already made strides in supporting foldable phones, while Apple is rumored to be working on its own foldable devices. As these new form factors become more prevalent, mobile OS will need to adapt to provide seamless user experiences across different screen sizes and interaction methods. Furthermore, the rise of AR will require mobile OS to offer robust AR development tools and APIs.
Finally, user privacy and security will remain paramount concerns. Both Apple and Google are under increasing pressure to protect user data and prevent privacy breaches. In the future, we can expect to see even stricter privacy controls, more transparent data usage policies, and enhanced security measures to combat malware and cyber threats. Here are some steps users and developers can take to enhance their privacy:
Actionable Steps for Developers and Users
- Prioritize User Privacy: Implement privacy-by-design principles in app development.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct routine security checks to identify and fix vulnerabilities.
- Stay Updated: Keep your OS and apps updated to benefit from the latest security patches.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication.
- Review App Permissions: Regularly check and adjust app permissions to limit data access.